Vgrid¶
Vgrid - A Python package for working with popular geodesic DGGS and graticule-based DGGS
Vgrid supports a wide range of popular geodesic DGGS, including H3, S2, A5, rHEALPix, Open-EAGGR ISEA4T, ISEA3H, DGGRID, DGGAL, EASE-DGGS, QTM, along with graticule-based DGGS such as OLC, Geohash, MGRS, GEOREF, TileCode, Quadkey, Maidenhead, and GARS.
Vgrid supports popular input and output GIS formats, including CSV, GeoJSON, Pandas/GeoPandas, Shapefile, GeoPackage, and GeoParquet.
Full Vgrid DGGS documentation is available at vgrid document.
To work with Vgrid DGGS directly in GeoPandas and Pandas, use the vgridpandas package. Full Vgridpandas DGGS documentation is available at vgridpandas document.
To work with Vgrid DGGS in QGIS, install the Vgrid Plugin.
To visualize DGGS in Maplibre GL JS, try the vgrid-maplibre library.
For an interactive demo, visit the Vgrid Homepage.
References:¶
- h3-py by Uber.
- s2sphere by Sidewalk Labs.
- a5-py by Felix Palmer and Thang Quach.
- rhealpixdggs-py by Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research.
- open-eaggr by Riskaware.
- EASE-DGGS by GEMS-UMN.
- pydggal by Jerome St-Louis from Ecere.
- DGGRID by Kevin Sahr.
- dggrid4py by Alex Kmoch.
- QTM by Thang Quach, with reference to QTM by Paulo Raposo.
- Lat Lon Tools QGIS Plugin by Calvin Hamilton.
- gars-field by Corteva Agriscience.
- Tilecode & Quadkey by Thang Quach, utilizing mercantile by Mapbox.
- antimeridian by gadomski.
- The DGGS Inspect feature in Vgrid is inspired by Area and shape distortions in open-source discrete global grid systems by Alex Kmoch et al. (2022) (resources).
- The Vgrid Document is inspired by leafmap developed by Qiusheng Wu from Open Geospatial Solutions.
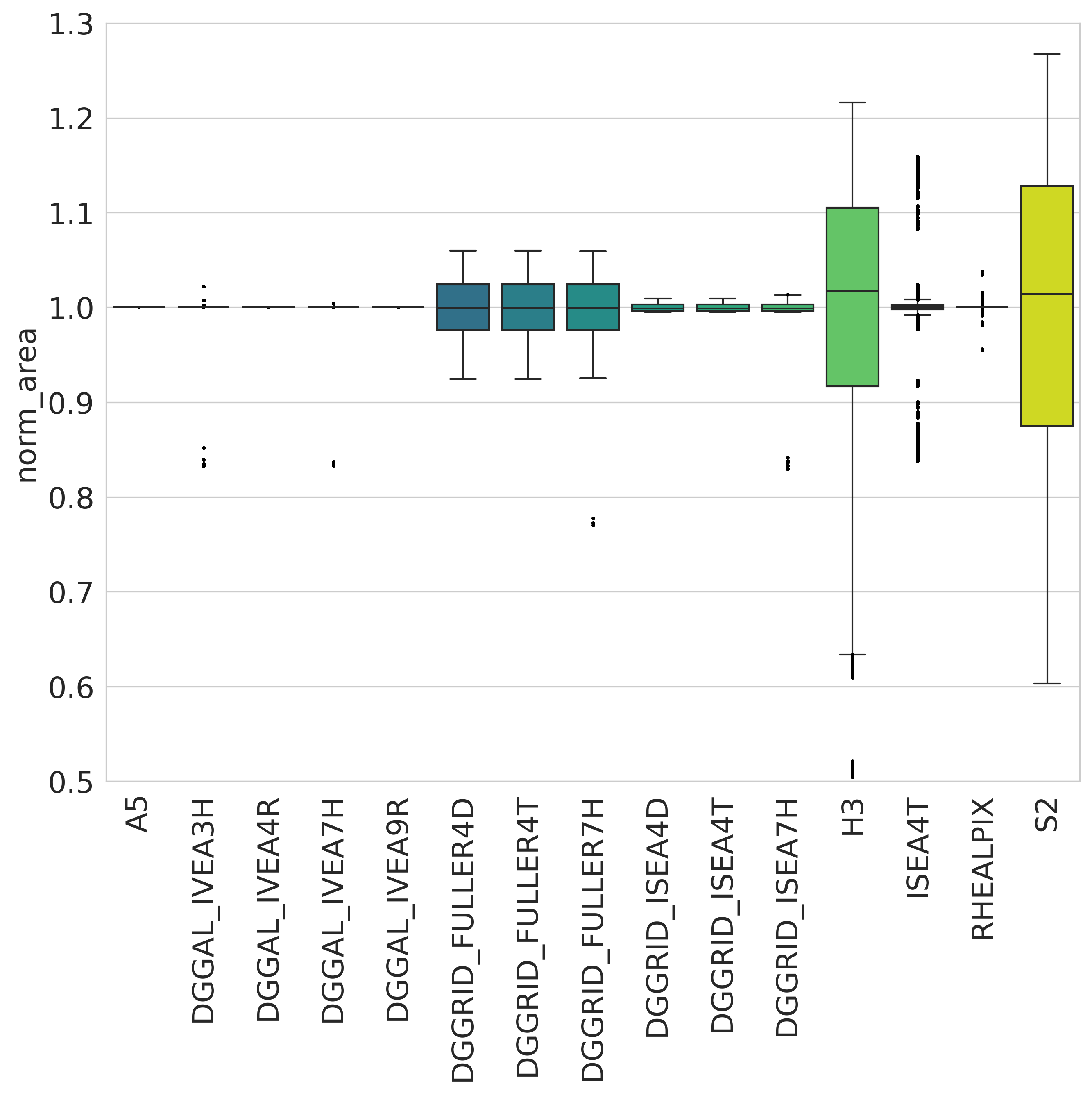
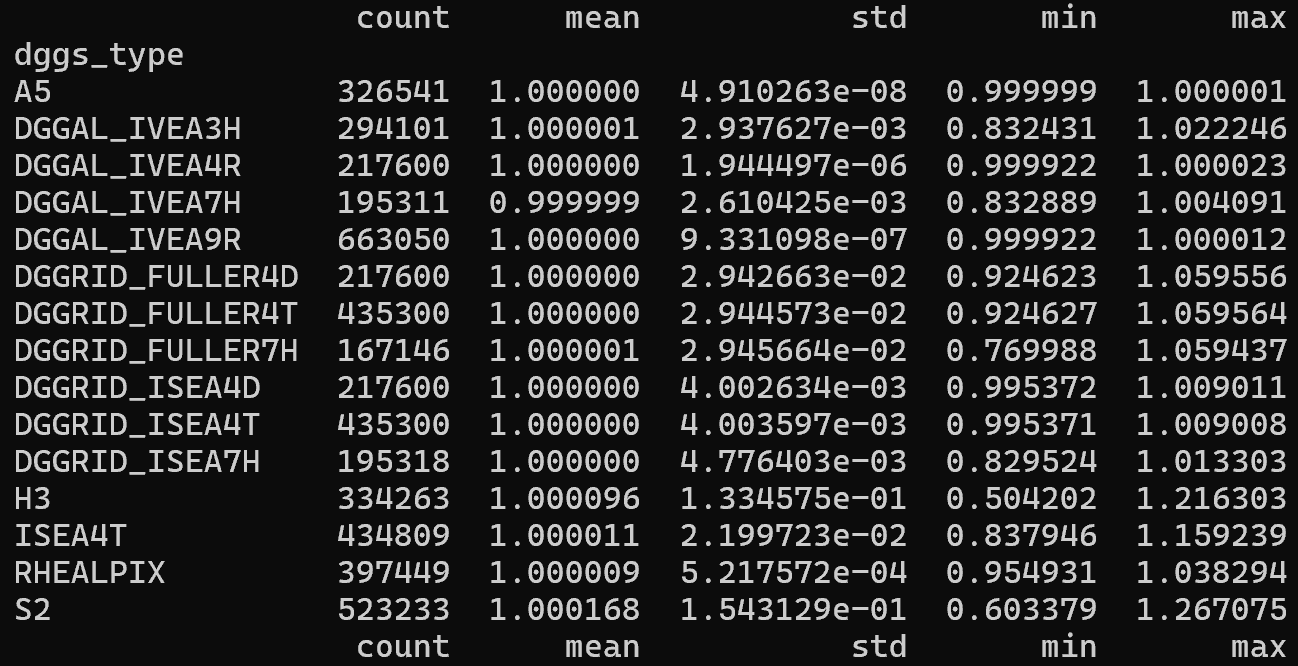
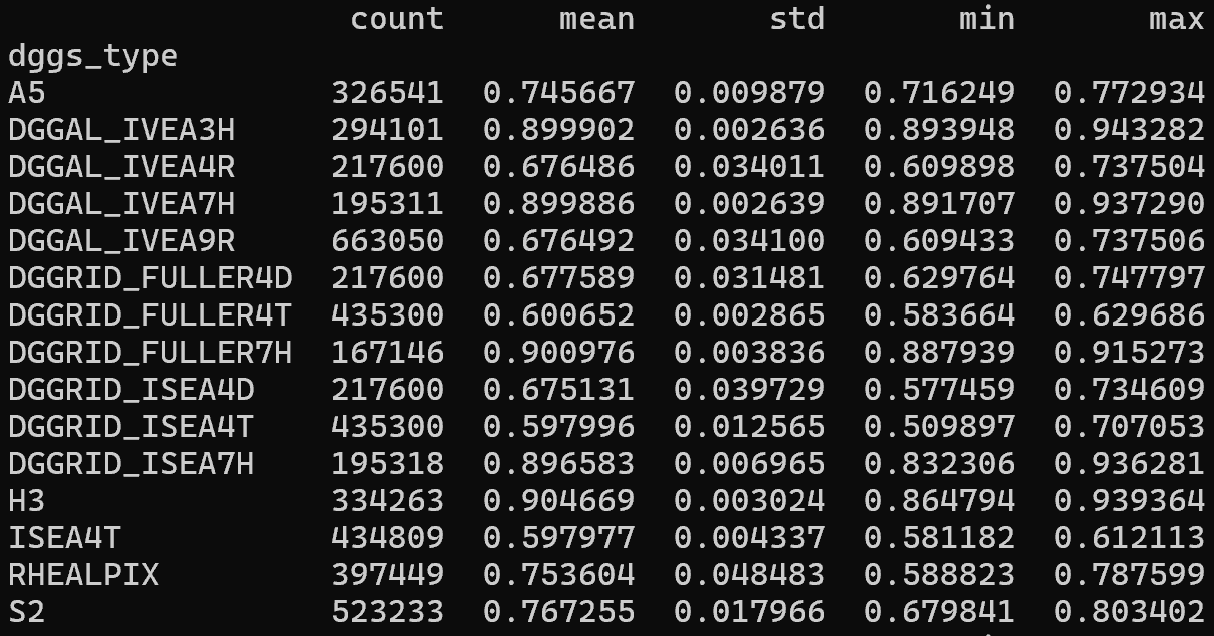
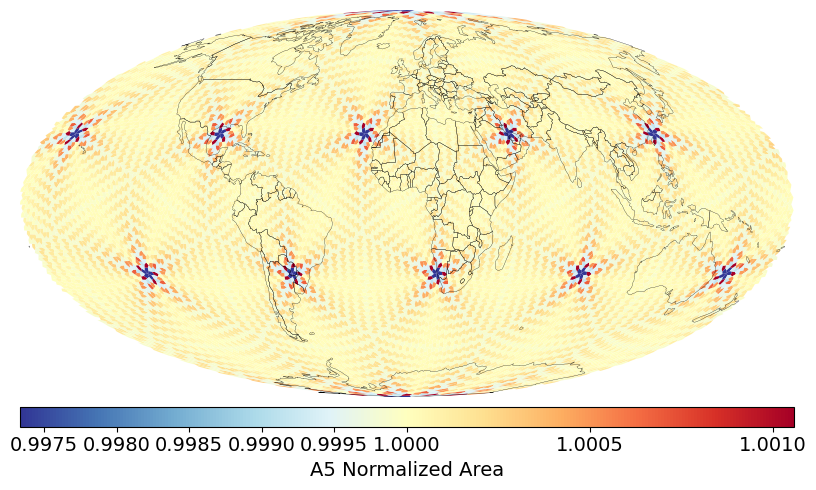
Area distortion over normalized areas of popular geodesic DGGS¶
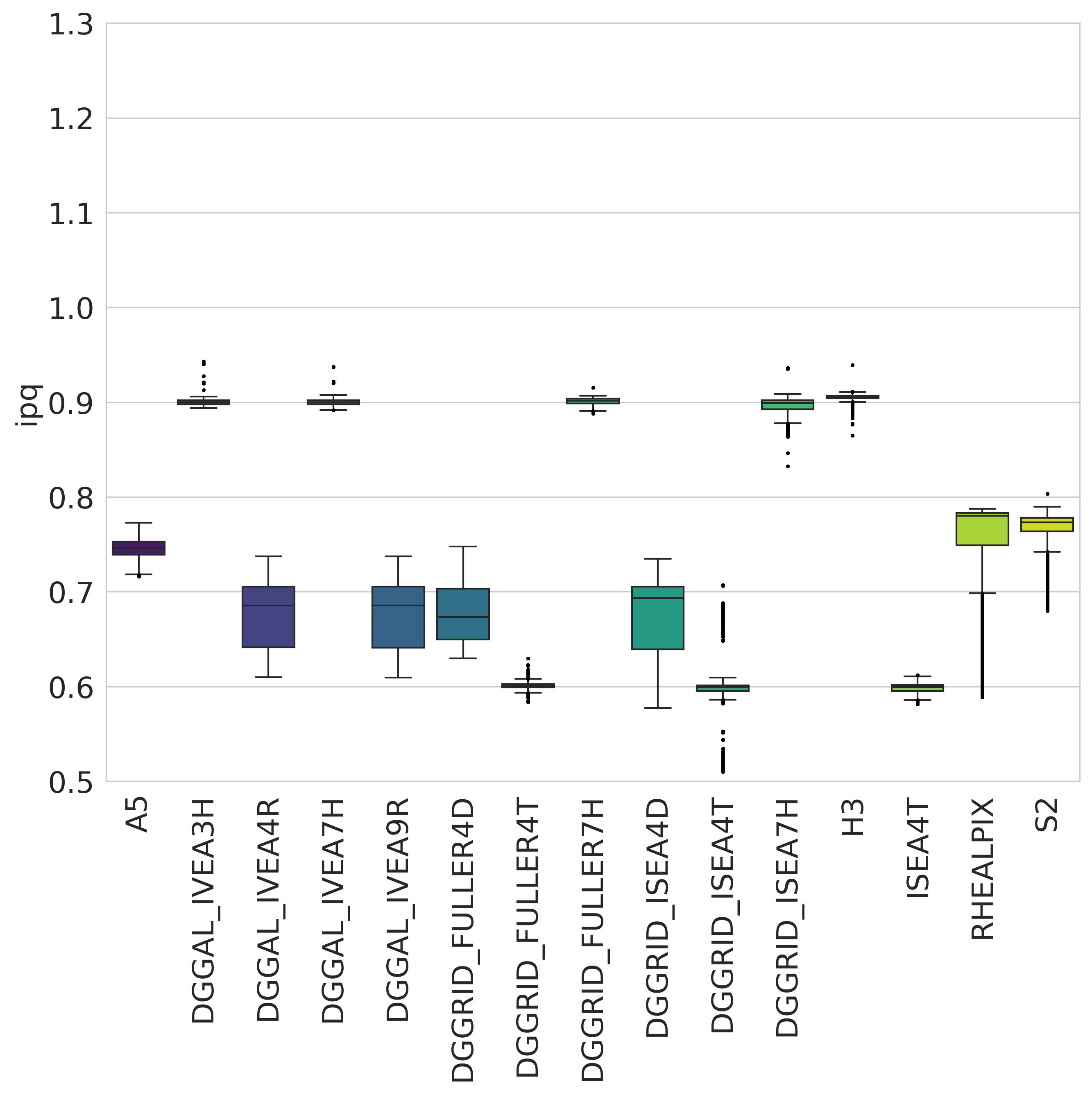
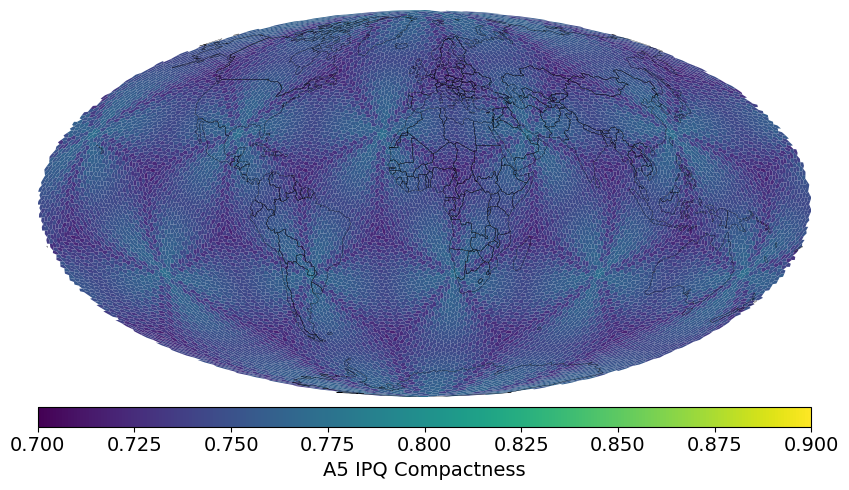
IPQ compactness distribution over popular geodesic DGGS¶
Isoperimetric Inequality (IPQ) Compactness (suggested by Osserman, 1987):
The range of the IPQ compactness metric is [0,1].
A circle represents the maximum compactness with a value of 1.
As shapes become more irregular or elongated, their compactness decreases toward 0.
Installation¶
pip¶
1 | |
Key Features¶
-
DGGS Conversion: Convert Latlon to DGGS, DGGS cells to Shapely Geometry/ GeoJSON, Vector to DGGS, Raster to DGGS.
-
DGGS Compact: Compact DGGS cells or expand them to a specific resolution.
-
DGGS Binning: Aggregate points into DGGS cells, supporting common statistics (count, min, max, etc.) and category-based groups.
-
DGGS Generator: Generate DGGS at a specfic bounding box and resolution.
-
DGGS Inspect: Calculate and visualize DGGS area distortions and IPQ (isoperimetric inequality) compactness at a specific resolution.
-
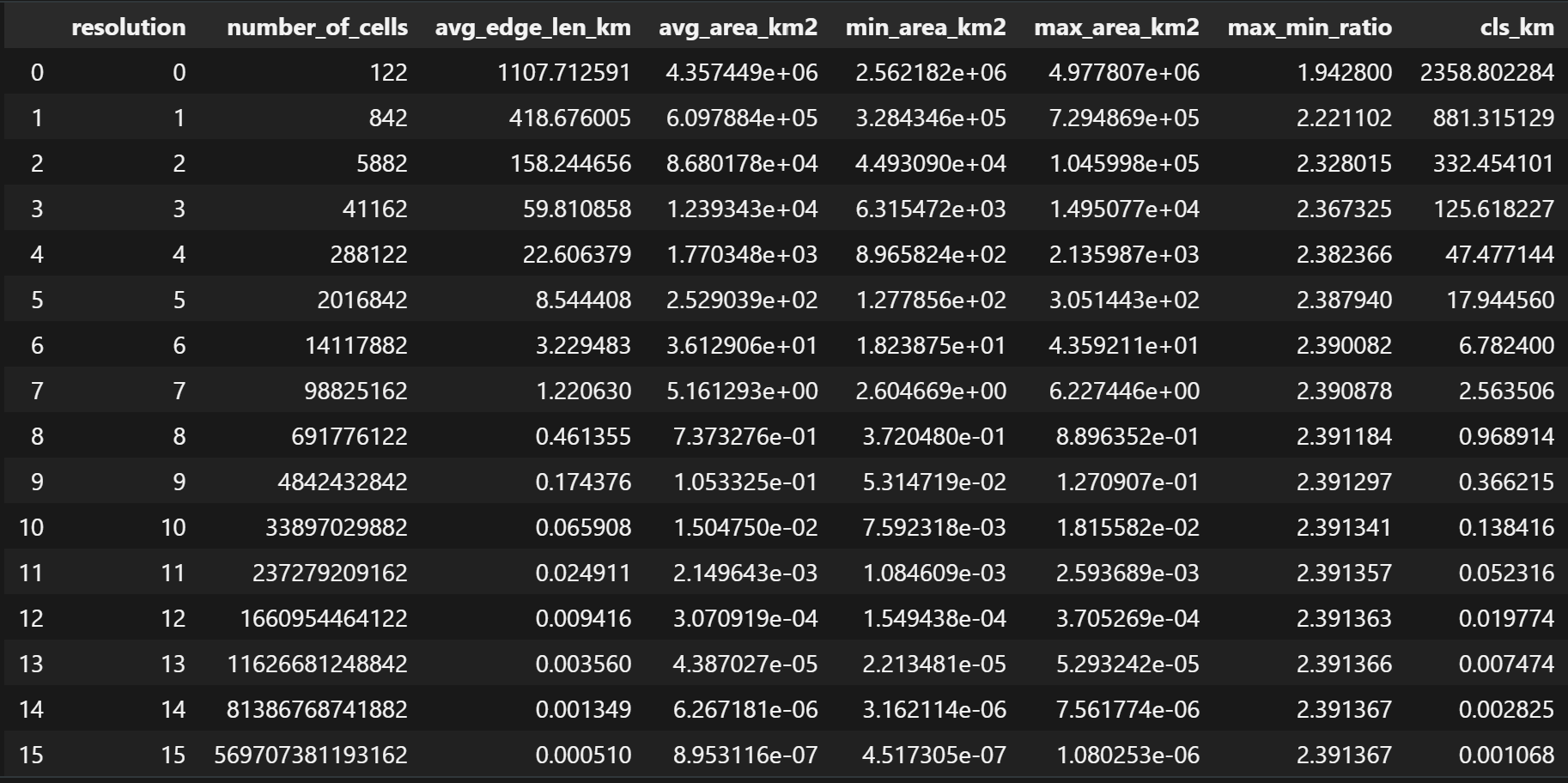
DGGS Stats: Show DGGS metrics for each resolution like number of cells, average edge length, average cell area, perimeter.
Usage examples¶
Latlon to DGGS¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
DGGS to Shapely Polygon¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
DGGS to GeoJSON¶
1 2 3 4 5 | |
Vector to DGGS¶
1 2 3 4 | |
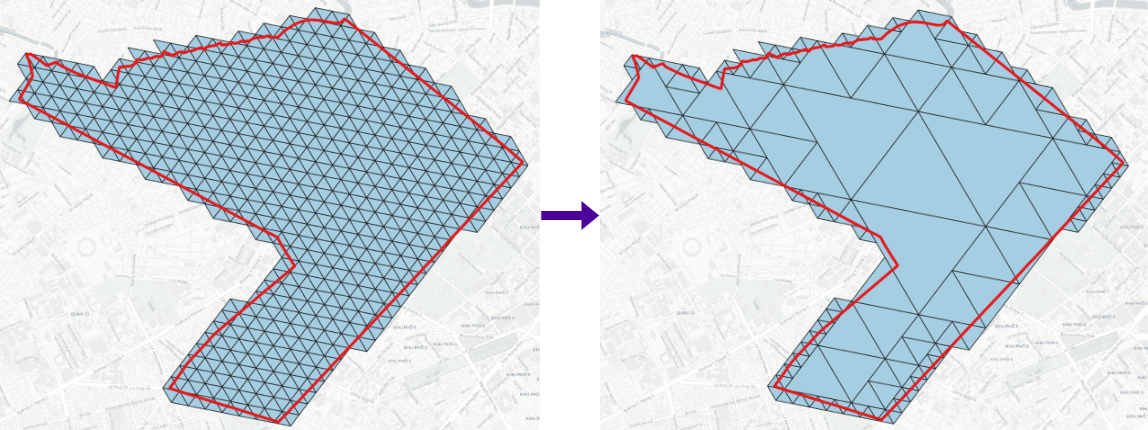
DGGS Compact¶
1 2 3 | |
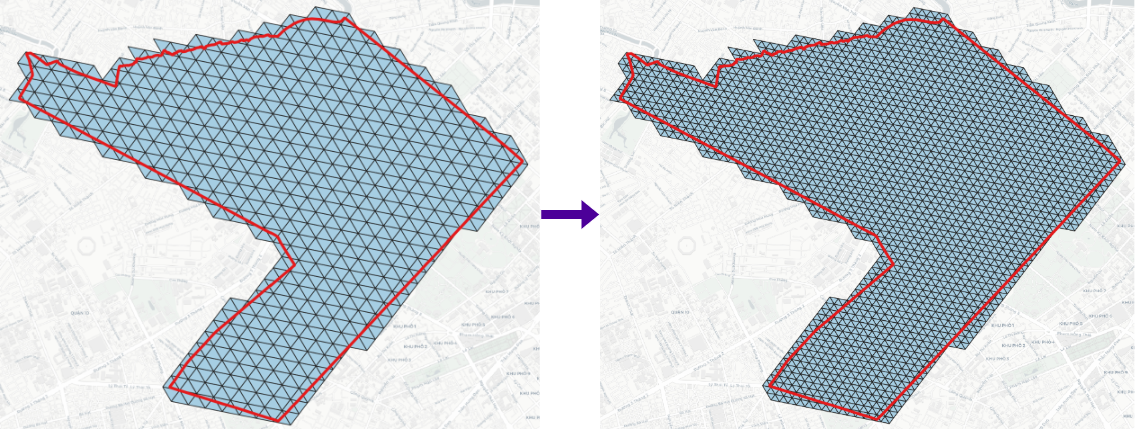
DGGS Expand¶
1 2 3 | |
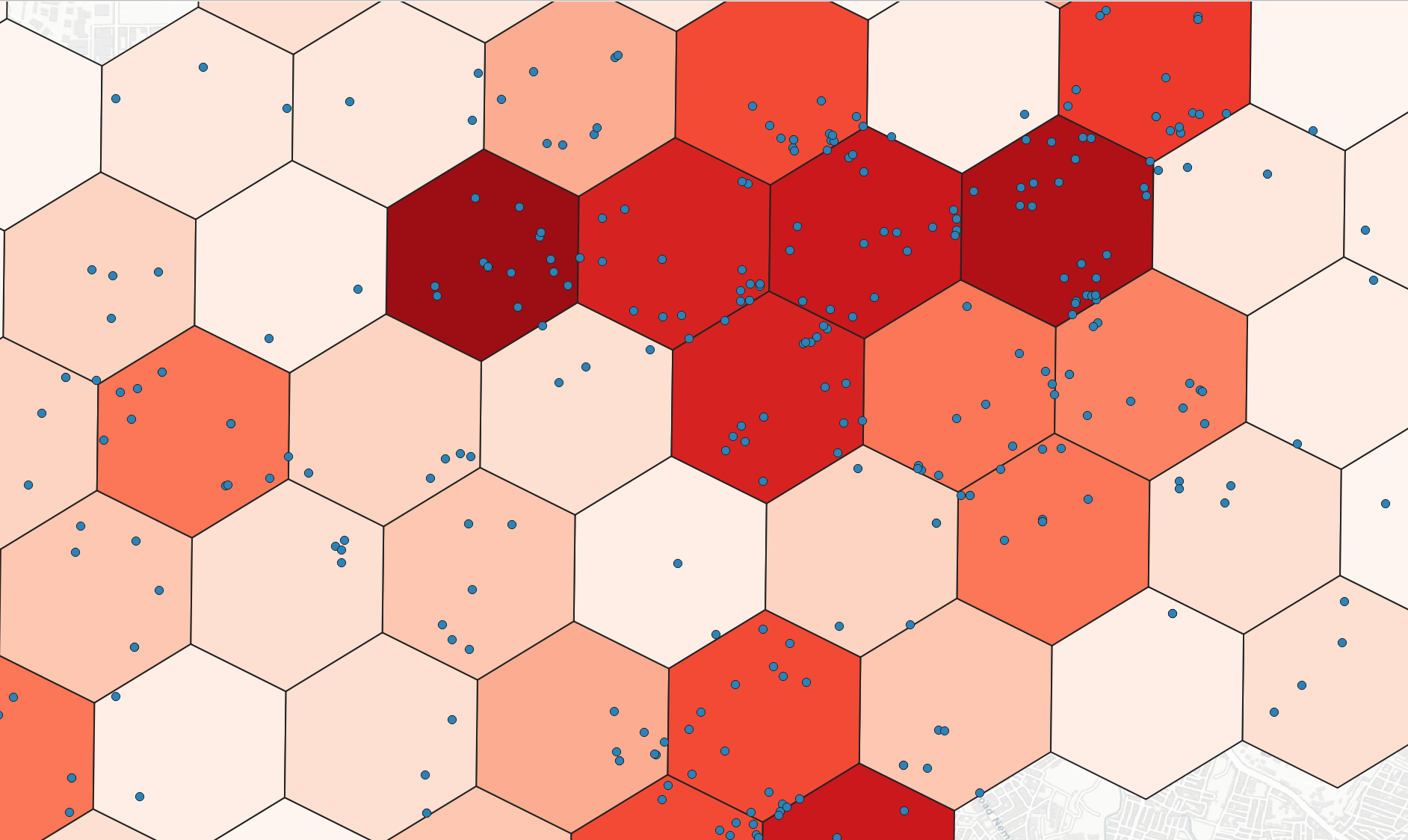
DGGS Binning¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
Raster to DGGS¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |

DGGS Generator¶
1 2 3 | |
DGGS Inspect¶
1 2 3 | |
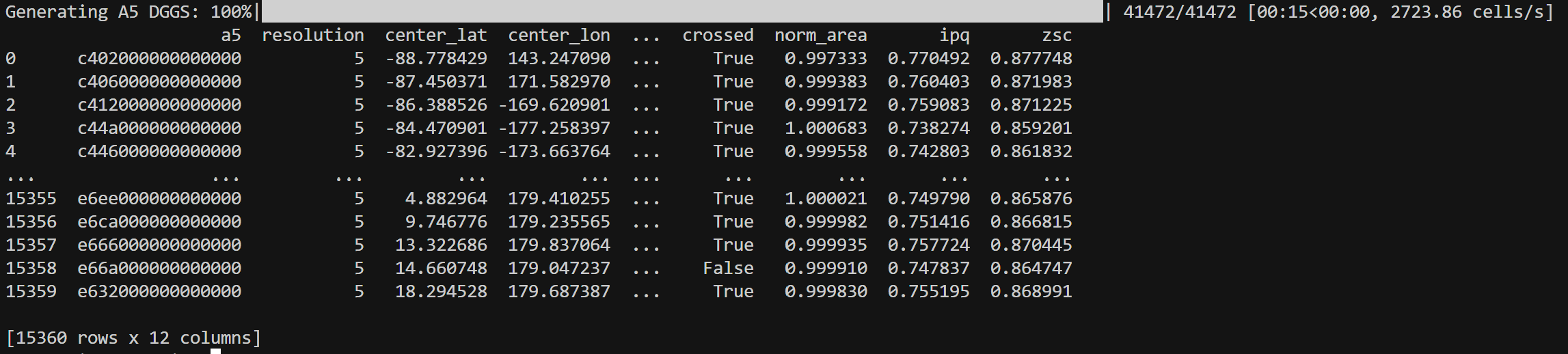
Distribution of DGGS Area Distortions visualized from DGGS Inspect¶
Visualization of DGGS IPQ Compactness visualized from DGGS Inspect¶
DGGS Stats¶
1 2 | |
Further examples¶
For more examples, see the example notebooks.